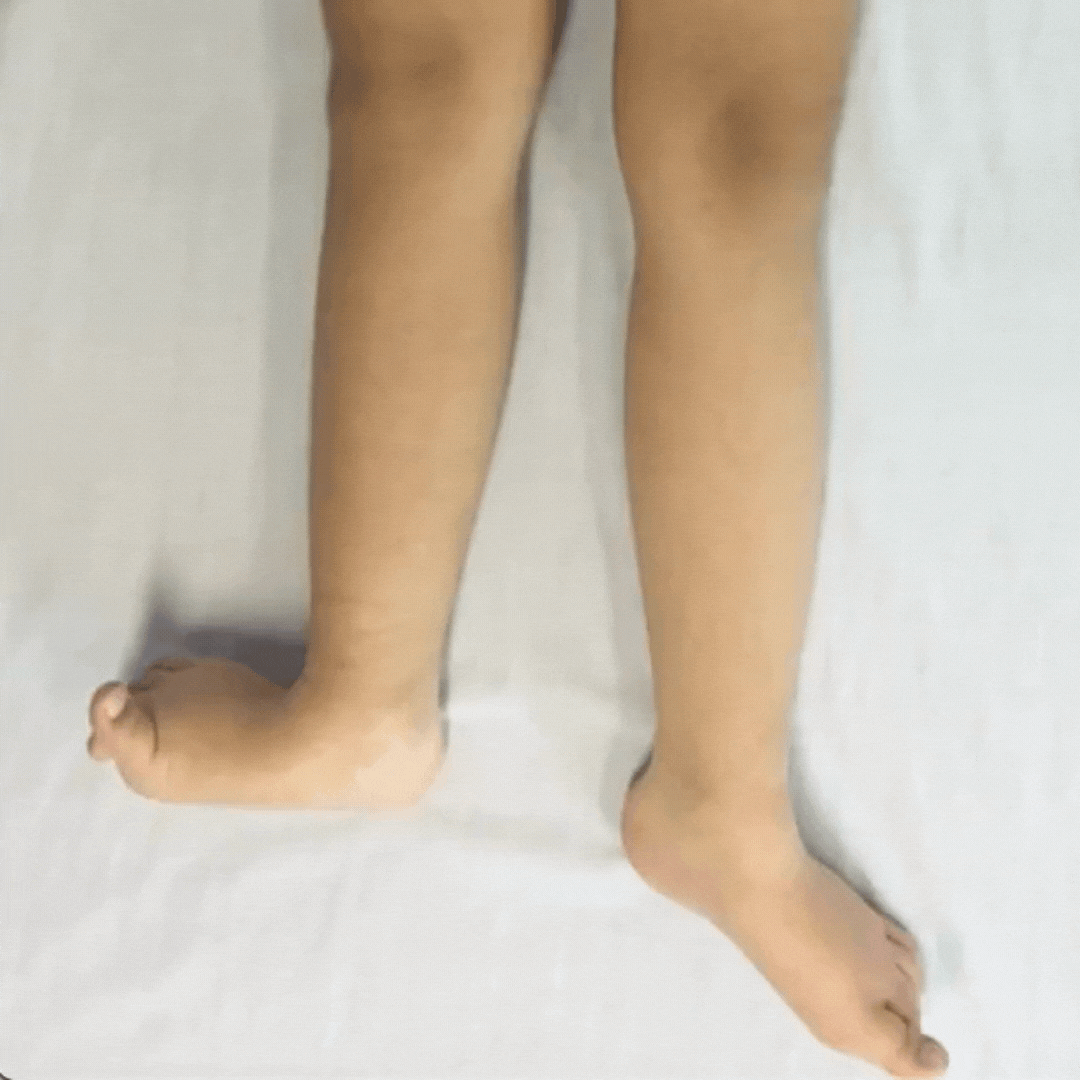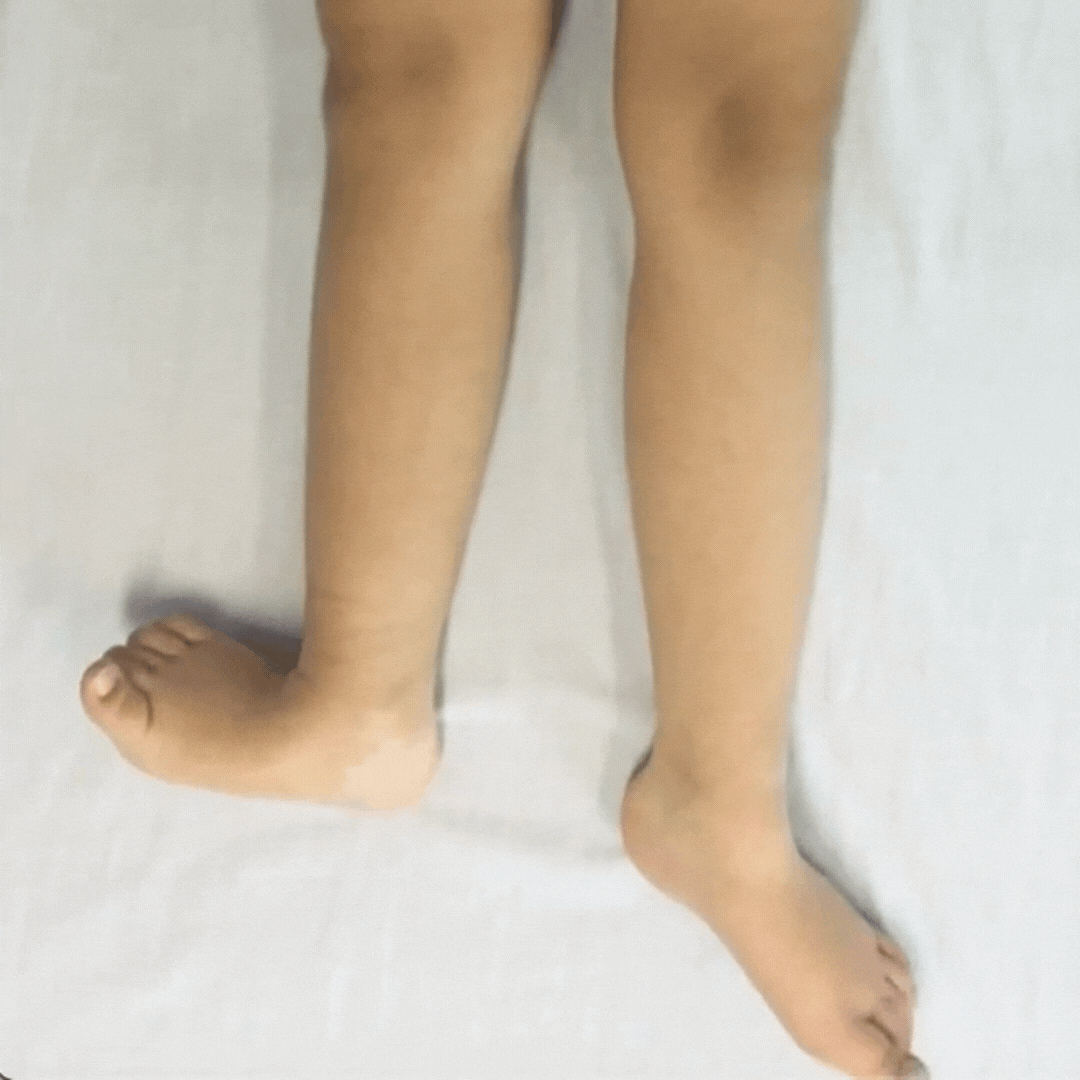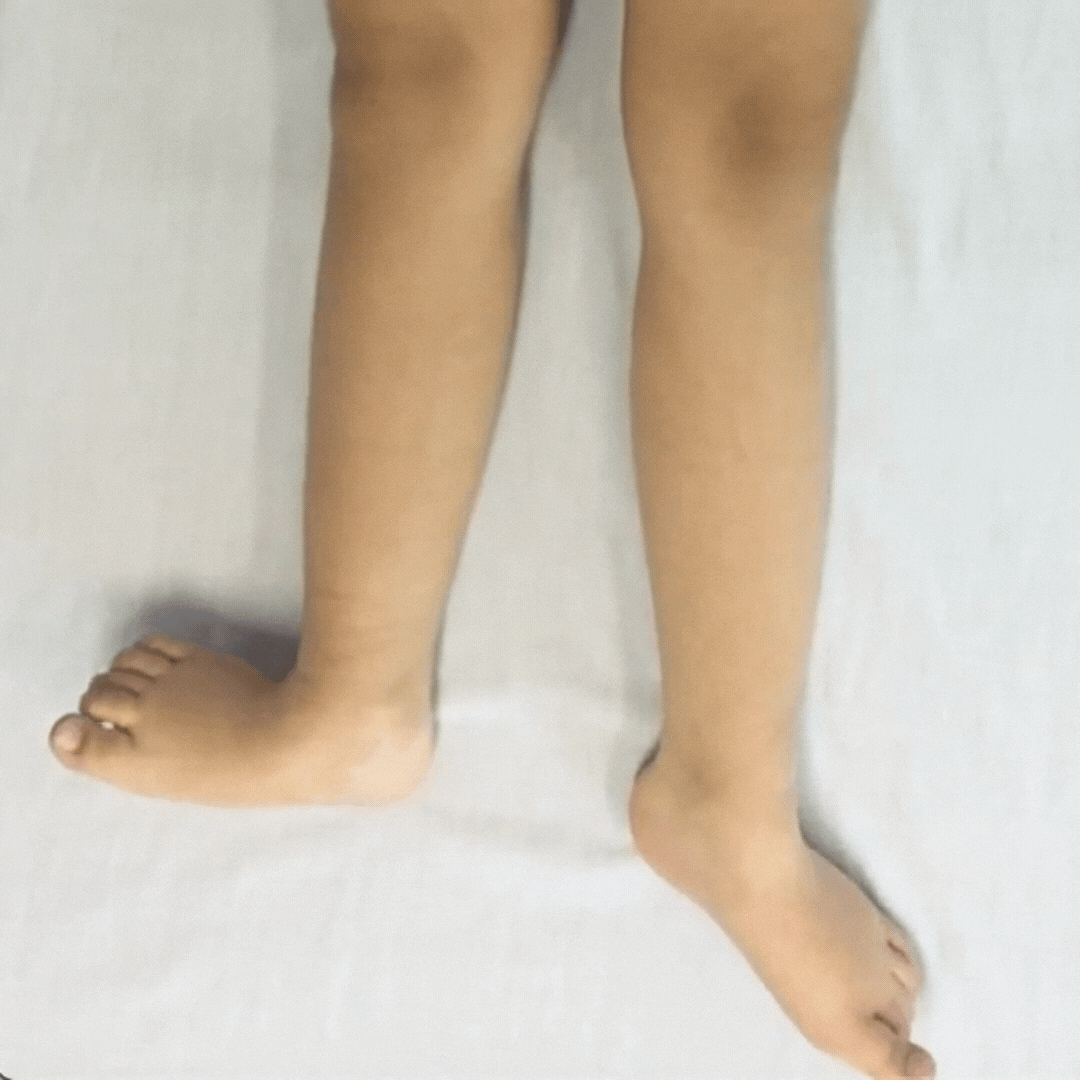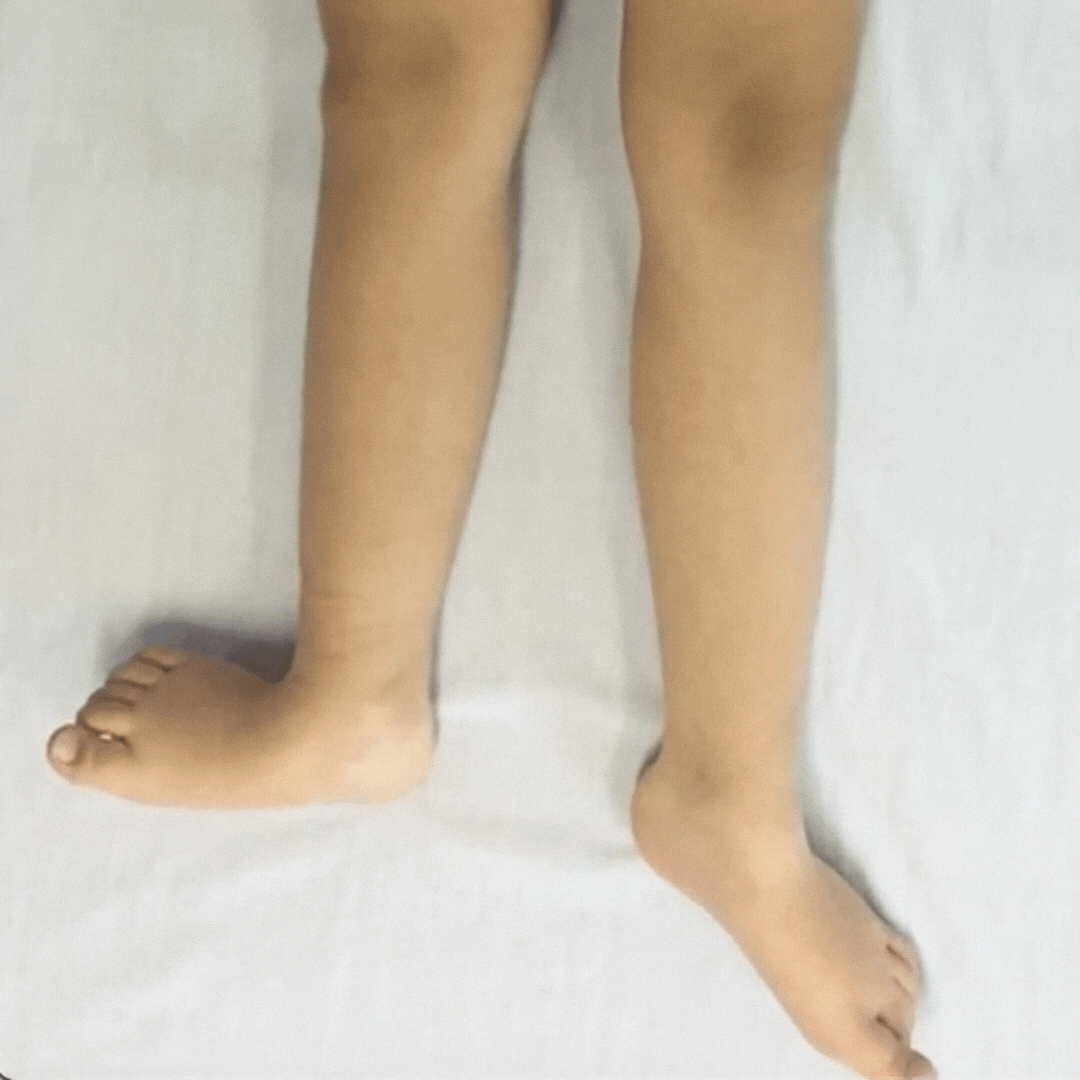
Children with dystonia have difficulties controlling movements as their muscle tone fluctuates, it varies moment-to-moment.
Dystonia is described as a movement disorder in which intermittent muscle contractions cause repetitive movements and abnormal postures.
Understanding how muscle tone is regulated and the role fascia plays in this regulation help us design strategies to help the child. We revisited these mechanisms previously in this post. The key concept to consider is the fact that fascia is richly innervated and it is considered the organ of proprioception* **.
In other words fascia plays an important role in how we feel our bodies and in muscle tone regulation.
There are two main ideas we have in mind while helping kids with dystonia:
Daily fascia therapy done by the parents helps with tone regulation. Our techniques improve the tension (the needed tension) in the fascial system. Having the right tension will help with the stability of the receptors that are fundamental for muscle tone regulation.
External wrapping (like the binder and wraps) and our ideas to play help organize the sensory system of the child bringing more control of the muscle tone.

When the child’s fascia gets more organized, the child gets calmer, there are less involuntary contractions. This is the first step to develop more accuracy in their fine motor skills and improve functionality.
You can book a Free Online Discovery Session to talk about the options we offer for you to learn how to do fascia therapy with your child. Book it here
WeFlow’s tip for you
You can help your child organize muscle tone by wrapping their hands. We are teaching you how to use a sock to wrap your child’s hand in the free preview of our course “10 ideas to develop your child’s hand”, watch it here (Idea #3)
—————
Ayudando con Distonía
Niños con distonía tienen dificultad para controlar sus movimientos ya que su tono muscular fluctúa, cambia todo el tiempo.
La distonía se conoce como un desorden del movimiento en el que contracciones involuntarias causan movimientos repetitivos y posturas anormales.
El entendimiento de cómo el tono muscular es regulado y el rol que tiene la fascia en esta regulación nos ayuda a desarrollar estrategias para ayudar al niño(a). Hemos hablado sobre esto es entradas anteriores, pero el concepto clave a considerar es el hecho de que la fascia está ricamente inervada y se le considera un órgano propioceptivo * **
Es decir, la fascia tiene un papel importante en cómo sentimos nuestro cuerpo y cómo regulamos el tono muscular.
Hay dos ideas principales que tomamos en cuenta cuando ayudamos niños con distonía:
La terapia de fascia diaria hecha por los padres ayuda a regular el tono muscular. Nuestras técnicas mejorar la tensión (buena y necesaria) dentro del sistema fascial. Al tener la adecuada tensión se logra dar estabilidad al receptor que es fundamental para la regulación del tono muscular.
Los sistemas de vendaje, como la faja y las envolturas, y nuestras ideas para jugar, ayudan a organizar el sistema sensorial del niño lo que resulta en un mejor control del tono muscular.

Cuando la fascia del niño se organiza, el niño se calma y hay menos contracciones involuntarias. Este es el primer paso para desarrollar más precisión en sus destrezas motoras finas y mejorar su funcionalidad.
Puedes solicitar una sesión exploratoria gratuita para conversar sobre las opciones que tienes para aprender cómo trabajar la fascia de tu hijo(a). Solicítala aquí
Tip WeFlow para ti
Puedes ayudar a tu hijo(a) a organizar el tono muscular a través de vendajes en sus manos. Te estamos enseñando cómo hacerlos con un calcetín, en nuestro curso “10 ideas para desarrollar las manos” en el que abrimos gratuitamente algunas lecciones. El curso está en inglés, pero seguro podrás entender las demostraciones.
Busca la opción “vista previa" aquí